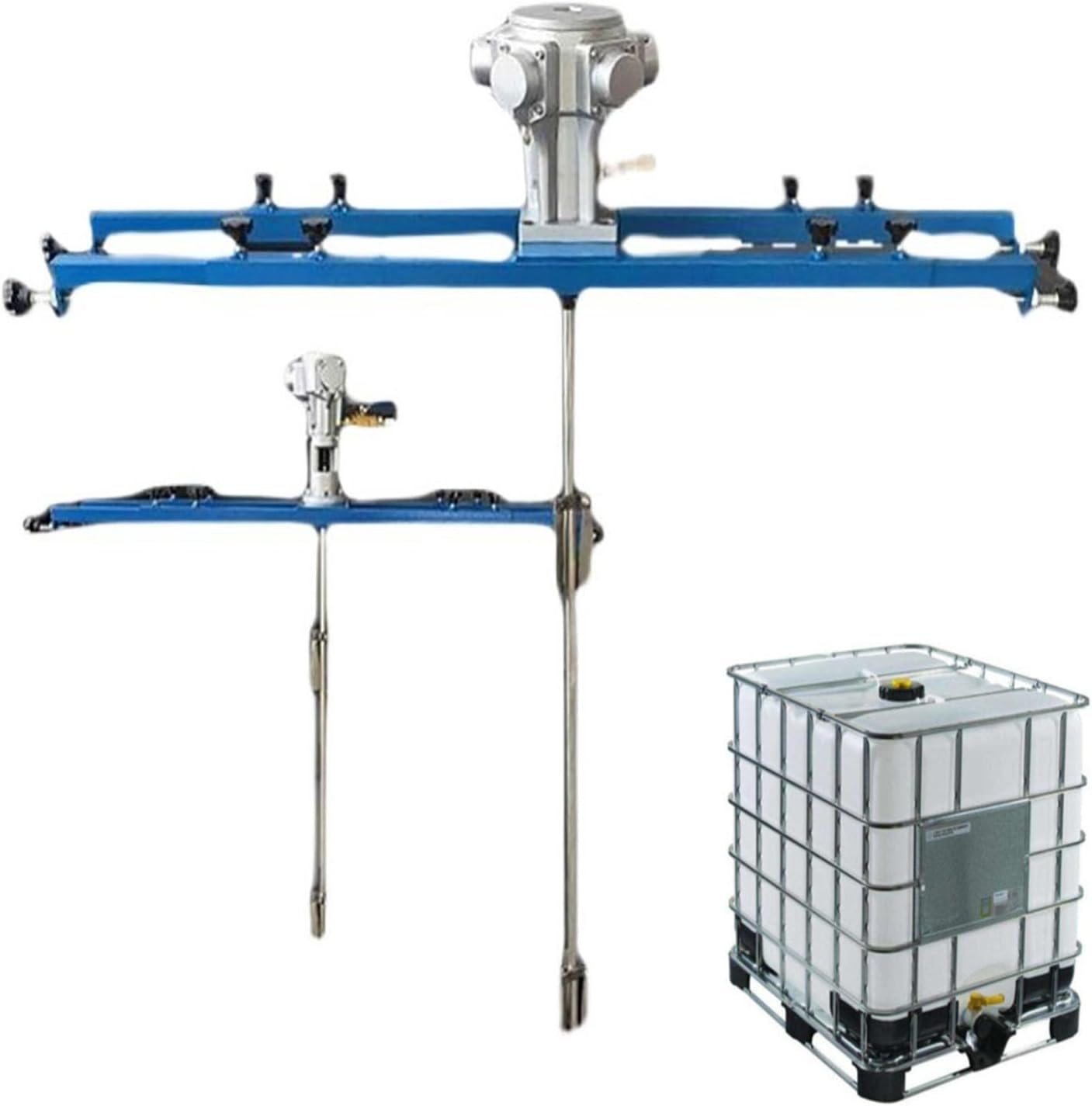
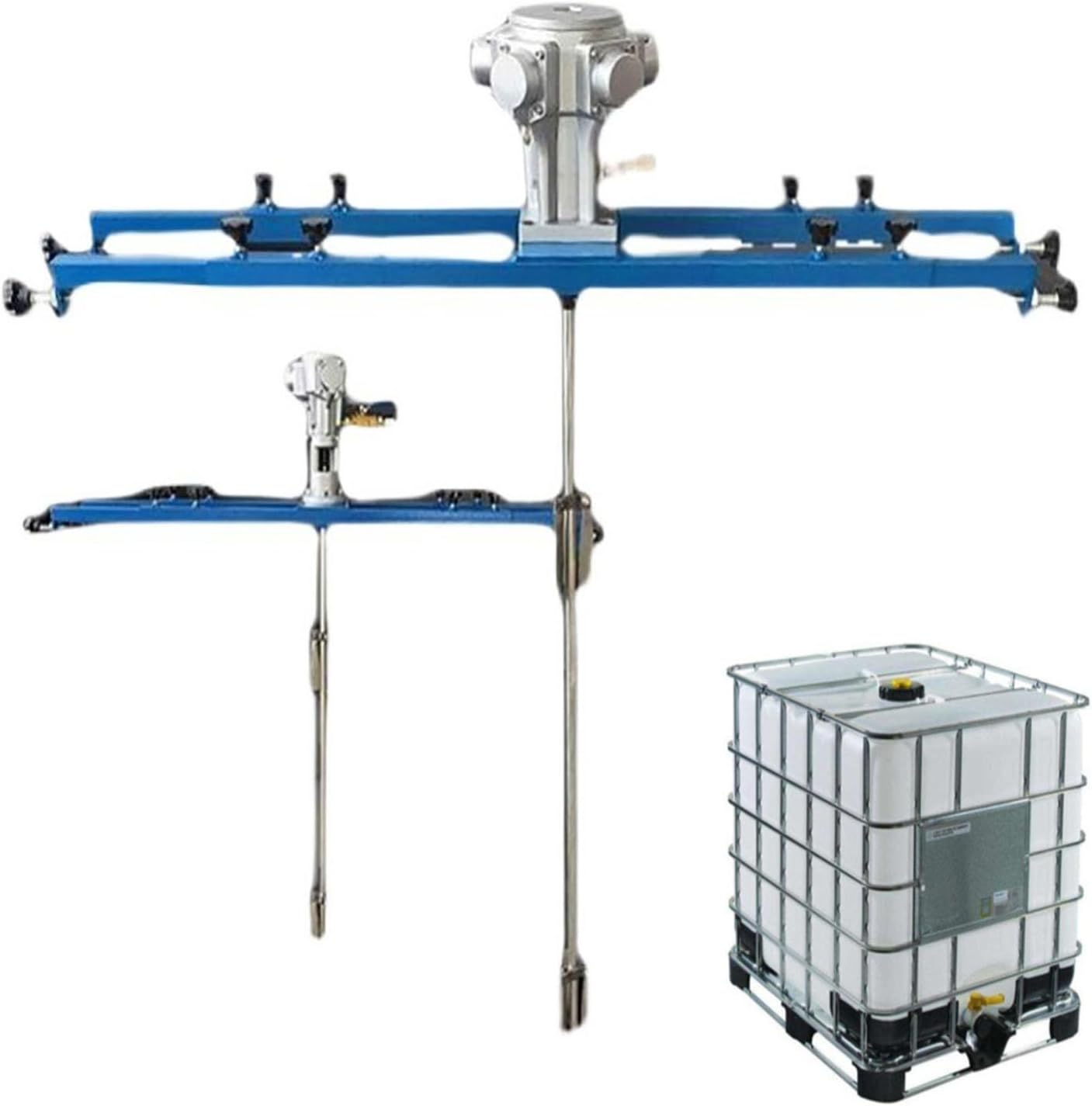
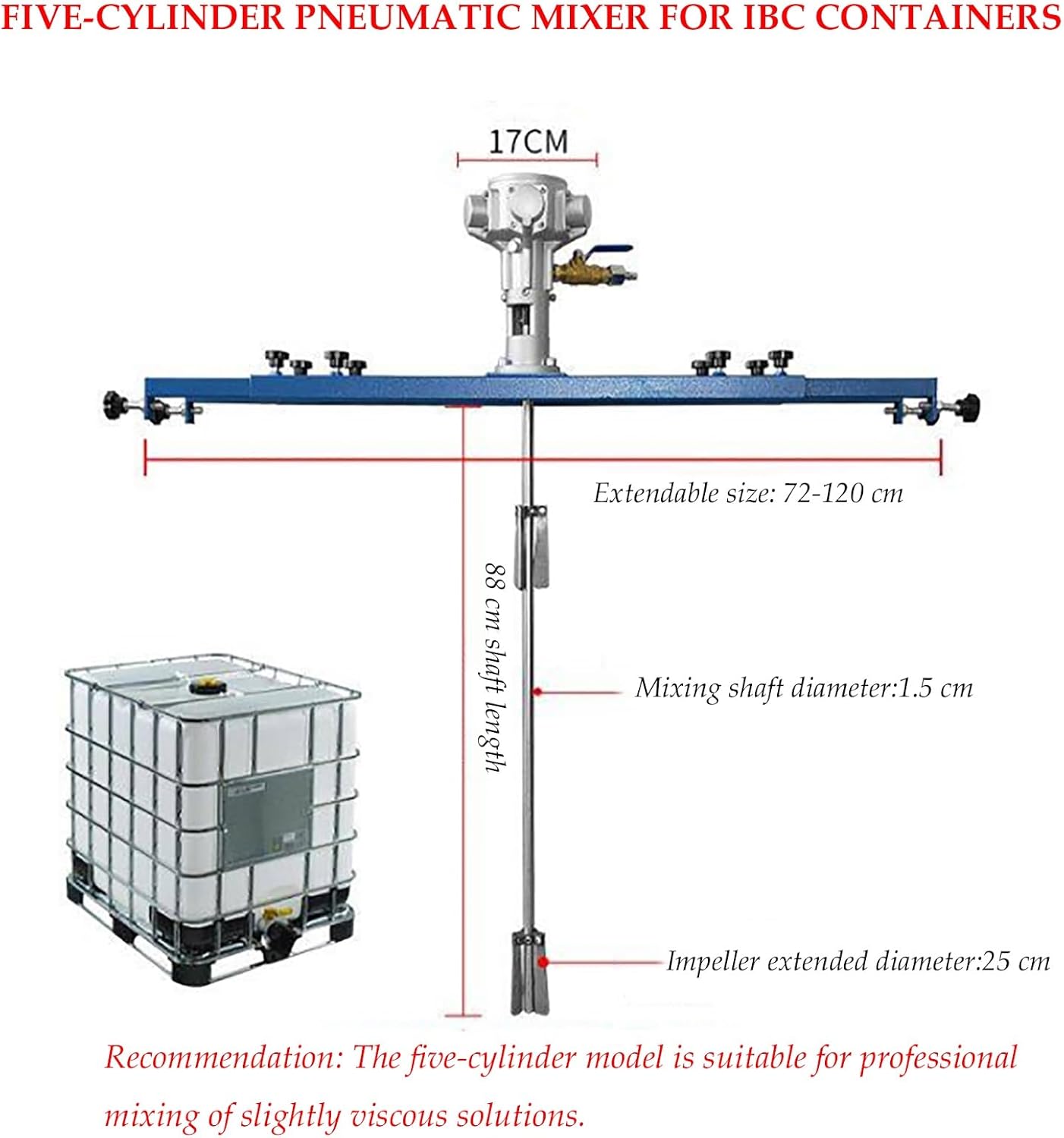
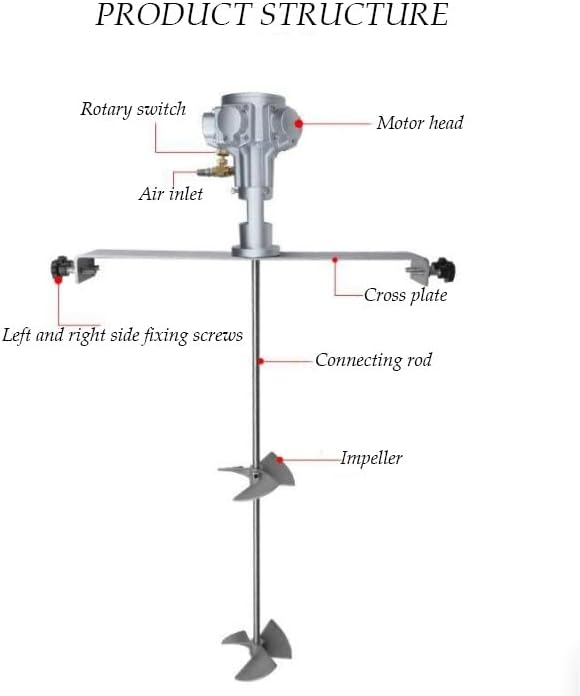
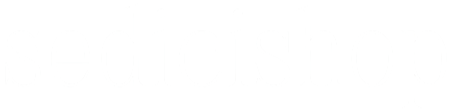Pneumatic Paint Mixer for IBC Open-top Drum, Coat Mixer Bracket Air Agitator Stirring Machine, Paint Mix Tool for Paint, Fluids, Manufacturing, Labs, Industrial Use(Five-cylinder)
Folding Propeller & Easy Installation: This Stainless Steel Folding Propeller fi
-
Detail
What is a pneumatic mixer?
A pneumatic mixer is an industrial mixing device that uses compressed air as a power source to drive the mixing blades, thereby mixing, dispersing, dissolving, or homogenizing materials.
Its core working principle is: using compressed air provided by an air compressor, it drives the rotor in the pneumatic motor to rotate, and then drives the mixing blades to rotate at high or low speed through a transmission shaft, causing convection and shearing of the materials in the container, ultimately achieving a uniform mixing effect.
Main Features
Explosion-proof safety
The pneumatic motor does not generate electric sparks during operation and operates at a low temperature, making it particularly suitable for use in hazardous environments with flammable, explosive, and dusty conditions, such as the chemical, petroleum, paint, and pharmaceutical industries.
Convenient speed adjustment
The mixing speed can be steplessly adjusted by regulating the pressure or flow rate of the compressed air, adapting to the mixing of materials with different viscosities and process requirements.
Overload protection
When the mixing load is too high, the pneumatic motor will automatically stop, preventing burnout due to overload and protecting the equipment and materials. It can be restarted immediately after the load returns to normal.
Simple structure and low maintenance costs
The pneumatic motor has fewer parts and a low failure rate. Routine maintenance mainly involves cleaning and lubrication, making it easier to maintain than electric mixers.
Applicable Scenarios
Chemical industry: Mixing paints, inks, adhesives, resins, etc.
Petroleum industry: Mixing crude oil, lubricating oil, fuel oil, etc.
Food and pharmaceutical industry: Mixing sauces, syrups, pharmaceuticals, culture media, etc. (food-grade materials are required).
Water treatment industry: Mixing chemicals, wastewater mixing, etc. -
Customer ReviewsNo comments